Difference between revisions of "Koman language"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
|name = Koman | |name = Koman | ||
|altname = | |altname = Qāmanşe | ||
|nativename = | |nativename = {{cs|DAD|. Qāmanşe .}} | ||
|pronunciation = [ | |pronunciation = [xɒmänʂe] | ||
|states (state) = [[Komania]] | |states (state) = [[Komania]] | ||
|region = Vaniua | |region = Vaniua | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|longd = | longm = | longEW = <!-- longitude degrees/minutes/direction --> | |longd = | longm = | longEW = <!-- longitude degrees/minutes/direction --> | ||
|ethnicity = Koman people | |ethnicity = Koman people | ||
|speakers = | |speakers = 48 million | ||
|date = 2015-2017 | |date = 2015-2017 | ||
|familycolor = vaniuan | |familycolor = vaniuan | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 4 January 2018
| Koman | |
|---|---|
| Qāmanşe . Qāmanşe . | |
| Pronunciation | [xɒmänʂe] |
| Region | Vaniua |
| Ethnicity | Koman people |
| Native speakers | 48 million (2015-2017) |
| Language family | |
| Early forms: | Proto-Vaniuan
|
| Dialects | Western Koman · Torosh · Bishe |
| Writing system | Vaniuan script, anciently Kalkali script |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | |
| Regulated by | State Academy of Linguistics |
| CWS code | DAD |
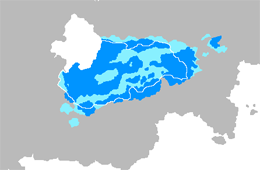 Dark blue = Majority; light blue = Sizable minority | |
Koman (Qālxārşē, /xɒlxɒrʂə/) is a Vaniuan language spoken in Komania. It has around 40 million native speakers and is mainly spoken by the Koman people in Komania and the Torosh region of Balakia. Koman belongs to the Kalkalic branch of the Vaniuan language family. Main influences can be attributed to Pre-Vaniuan and Mahavic languages with some loanwords mainly of Shohuanese and Amaian origin. The most noticeable distinctions between Koman and other Vaniuan languages is the large corpus of Mahavic loanwords and lack of gender which is only seen in certain pronouns.
Geographic distribution
Name
The language is natively known as Qālxārşē or Qālxār şēşdhēm, pronounced /xɒlxɒrʂə/ or /xɒlxɒr ʂəʂðəm/ accordingly.
Classification
Koman is a member of the Kalkalic branch of the Vaniuan family of languages; the language itself is part of a dialectal continuum where mutual intelligibility can be seen in different degrees.
Koman has a basic degree of vowel harmony and is a fusional language which lacks any grammatical gender, its natural word order is SVO but can be written in SOV order in poetry or official documents.
Today modern Koman uses the Qālxār (Western Koman) dialect heavily based on its Classical predecessor as the standard variant, other dialects include the Bīşē and Tārāş varieties.
Dialects
The Koman language is comprised of 3 main varieties: Western Koman (Qālxār), Central (Bīşē) and Eastern (Tārāş), these are usually regarded as dialectal groupings comprising several subdivisions rather than individual dialects.
Western Koman
History
The first records of the earliest form of the language can be traced back to the 7th century where inscriptions in stone pillars were found in the eastern region of the northern Vaniuan steppes, thanks to archaeological evidence and early records from the inhabiting peoples of the region, it can be estimated that the Kali people spoke initially a variation of Old Mahavic but became gradually assimilated by their larger Vaniuan neighbours, who at the time spoke a late form of Proto-Eastern Vaniuan which due to the harsh environment lived equally as nomads. The increasing assimilation of Kali people led to the creation of a tribal confederation estimated to have been around 100-500CE which gave rise to the later forms of the Kalkali language and people.
Modern Koman is considered as a direct descendant of the later forms of the Kalkali language, the language of the Kalkali nomads who inhabited the northern steppes of Vaniua and of great literary development in the realms of Şī Āşar during and after the rise of the Great Horde. The now extinct Mahavic Oshar language, once spoken by the Oshar dynasty left profound influences on both levels of morphology and vocabulary. By the 17th century, Classical Koman arose as the common tongue of the Komans, Şādhëşkan Hacām, a prominent polymath, became the greatest representative of the Koman language, his efforts led the introduction of the language to the court and nobility, after his work in the book "Ëbëm Mothāh: Vā thum kādhulim " (Speech of the Common: Language of greatness) being renowned by the emperor himself. By the 18th century, a regularised version of the language was made based on the Jovaic dialectal grouping, having preserved most foreign loanwords because of matters of cultural heritage and conservatism.
The term "Koman" itself can vary depending on the dialect, before the 19th century, the language was known according to the name of the dialect spoken, this changed with the orders of prime minister Racan Ācom, who for matters of ethnic unification and nationalism, decided to unify the term. The most prominent names prior the unification were either "Kālyāghār" or "Jānva" with "Kāman" being used to refer to the dialect spoken in court.
The short-lived state of Kadhan used the term "Kāman" to refer to the language, with a high degree of Amaian loanwords seen prior to the 19th century.
Phonology
Consonants
The following tables lists the consonants and vowels of the standard Koshaivic dialect. The consonants enclosed in parentheses are considered as allophones.
| Bilabial | Labio-dental | Dental | Alveolar | Post-alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Labio-velar | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | ||||||||
| Plosive | p b | t d | k g | q | |||||||
| Fricative | β | f | θ ð | s z | ʒ | ʂ ʐ | x | ʁ | h | ||
| Affricate | |||||||||||
| Approximant | j | w | |||||||||
| Rhotic | r | ||||||||||
| Lateral app. | l |
Vowels
| Front | Near-front | Central | Near-back | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i (i:) y | u (u:) | |||
| Near-close | |||||
| Close-mid | e | o (o:) | |||
| Mid | ə | ||||
| Open-mid | |||||
| Near-open | |||||
| Open | ä | ɒ |
Phonotactics
Orthography
Grammar
Morphology
Literature
Writing system
Vocabulary
Examples
Seasons
| English | Koman |
|---|---|
| spring | qam |
| summer | kēr |
| autumn | bē |
| winter | şohma |
Numbers
| Number | Koman | Number | Koman |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | mā | 10 | qām |
| 1 | şe | 20 | sox qām |
| 2 | soxu | 30 | mez qām |
| 3 | meza | 40 | sah qām |
| 4 | sağa | 50 | şew qām |
| 5 | şew | 60 | bah qām |
| 6 | bako | 70 | şēh qām |
| 7 | şēhēn | 80 | yez qām |
| 8 | yeza | 90 | diti qām |
| 9 | dit | 100 | dena |
| 1000 | teşa |
Colours
| English | Koman |
|---|---|
| black | şērē |
| blue | sāğadaş |
| brown | shāğ |
| grey | kēr |
| green | şēğad |
| orange | TBA |
| pink | şēnēdēş |
| purple | TBA |
| red | tēsē |
| white | shāna |
| yellow | şāza |