Difference between revisions of "Kwalia language"
Anonymous123 (talk | contribs) |
Anonymous123 (talk | contribs) m (→Phonology) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
===Phonemes=== | ===Phonemes=== | ||
Tayam has | Tayam has 21 phonemic consonants and 7 phonemic vowels, fairly average cross-linguistically but perhaps unusual for many Ngerupic languages. It is similar in size to the inventory of the more dominant [[Awatese language]]. | ||
====Consonants==== | ====Consonants==== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | ||
|- style="font-weight:bold;" | |- style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | ||
! Consonants | ! style="background-color:#c0c0c0;" | Consonants | ||
! Bilabial | ! Bilabial | ||
! Labiodental | ! Labiodental | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
! Glottal | ! Glottal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Nasal | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Nasal | ||
| m | | m | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Plosive | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Plosive | ||
| p pʰ | | p pʰ | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
| ʔ | | ʔ | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Fricative | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Fricative | ||
| | | | ||
| v | | v | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
| h | | h | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Affricate | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Affricate | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Lateral approximant | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Lateral approximant | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Lateral flap | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Lateral flap | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Approximant | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Approximant | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
'''Notes:''' | '''Notes:''' | ||
* Intervocalically, /v/ is realized as the labiodental flap [ⱱ]. | |||
* Intervocalically, /l/ is usually realized as a tap [ɾ]. | |||
* Unaspirated voiceless plosives often voice word-initially: /p t c k/ [b d ɟ g]. | |||
====Vowels==== | ====Vowels==== | ||
| Line 138: | Line 141: | ||
! style="background-color:#c0c0c0;" | Vowels | ! style="background-color:#c0c0c0;" | Vowels | ||
! Front | ! Front | ||
! Central | |||
! Back | ! Back | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Close | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Close | ||
| | | i | ||
| ʉ | |||
| u | |||
|- | |||
| style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Close-mid | |||
| e | |||
| | | | ||
| | | o | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Open | | style="font-weight:bold; background-color:#efefef;" | Open | ||
| | | a ã | ||
| | |||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
```Notes:``` | |||
* The central close vowel is often opened to [ə] when unstressed. | |||
* Close-mid vowels often become open-mid in closed syllables: /e o/ [ɛ ɔ] | |||
===Phonotactics=== | ===Phonotactics=== | ||
TBD | |||
==Morphology and syntax== | ==Morphology and syntax== | ||
Revision as of 05:16, 9 October 2021
| Tayam | |
|---|---|
| üchã | |
| Pronunciation | [ʉt͡ʃã] |
| Region | southern Awating (Nguxi Province, Nąnim Province) |
| Ethnicity | Tayam |
| Native speakers | 3,900 (2020) |
| Language family | Language isolate |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | none |
| CWS code | ytm |
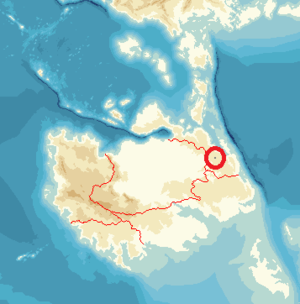 | |
Tayam is a language isolate spoken by about 3,900 people in southeastern Awating.
Origins and discovery
Tayam's origins are unknown and the subject of controversy. Study of Tayam began in 1961 with the Awatese linguist Kama Řąziya Ngunim Ningną. Kama disappeared under mysterious circumstances after venturing from Kąkoma to the valleys of southern Awating, and his notes were published posthumously as Characteristics of the Teyam Language: A Preliminary Sketch. This put off many other linguists from attempting further study, and information from then on was few and far between. There were very few speakers willing to provide the linguists with any information, and Tayam was thought to be extinct from about the 1990s until about 2014. In 2020, the case of Tayam was revisited, facilitated by improved availability of travel resources and more linguistic knowledge, and the speaker numbers in local academic circulation were updated.
Classification and number of speakers
Tayam has been proven to be a language isolate, unrelated to any other languages. There have been numerous controversies about its classification, stemming from prior lack of reliable information about the language. However, as the Tayam-speaking area became more accessible and more recent data was obtained, the few scholars studying the language began to question their earlier classifications, and Tayam remains yet to be conclusively classified; current scholarly consensus and data suggest that Tayam is a language isolate. Tayam is also unusual in that, despite Awating's repressive and hostile indigenous language policy, the language's vitality is stable and even vigorous; despite the small size of the speech community, many Tayam are monolingual or speak little Awatese, rates of inter-generational transmission are very high, and the speakerbase generally lacks a negative attitude toward the language. Tayam is spoken natively by about 3,900 people across several villages in Awating.
From when study of the language began in the early 1960s to about 2014, very little reliable data was available about the language, due to the relative inaccessibility and isolation of the Tayam-speaking area as well as the small number of speakers. While the sparse data did suggest that it may have been an isolate, linguists at the time generally classified Tayam as a Ngerupic language, owing to a few shared areal features in common with the Ngerupic languages of Awating. Some scholars have also claimed that Tayam was invented by groups of rural bandits as a method of concealing information, citing its areally unusual phonology and grammar and lack of consensus about the language's origins.
Linguist Amang Řąziya Ngunrą Zahang has posited that Tayam is related to the Ngigu language of southern coastal Awating, and therefore related to the Abugo languages of Lahan via an Umo-Abugo language macrofamily. Neither proposal has been accepted by mainstream academia, and these are both regarded as fringe theories.
Phonology
Phonemes
Tayam has 21 phonemic consonants and 7 phonemic vowels, fairly average cross-linguistically but perhaps unusual for many Ngerupic languages. It is similar in size to the inventory of the more dominant Awatese language.
Consonants
| Consonants | Bilabial | Labiodental | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Palatal | Labiovelar | Velar | Glottal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||||
| Plosive | p pʰ | t tʰ | c cʰ | k kʰ | ʔ | |||
| Fricative | v | s | ʃ | h | ||||
| Affricate | t͡ʃ | |||||||
| Lateral approximant | l | |||||||
| Lateral flap | ɺ | |||||||
| Approximant | j | w |
Notes:
- Intervocalically, /v/ is realized as the labiodental flap [ⱱ].
- Intervocalically, /l/ is usually realized as a tap [ɾ].
- Unaspirated voiceless plosives often voice word-initially: /p t c k/ [b d ɟ g].
Vowels
| Vowels | Front | Central | Back |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | ʉ | u |
| Close-mid | e | o | |
| Open | a ã |
```Notes:```
- The central close vowel is often opened to [ə] when unstressed.
- Close-mid vowels often become open-mid in closed syllables: /e o/ [ɛ ɔ]
Phonotactics
TBD