Difference between revisions of "Vemkha language"
m |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|name = Vemkha | |name = Vemkha | ||
|altname = | |altname = | ||
|nativename = | |nativename = Vəmɣə ɣuɣs, Vəŋx kuɣs, Wamx kuɣs | ||
|pronunciation = {{IPA|[ | |pronunciation = {{IPA|[[Vemkha language#Phonology|[vəmɣə]]]}}, {{IPA|[[Vemkha language#Phonology|[wamx]]]}}, {{IPA|[[Vemkha language#Phonology|[vəŋx]]]}} | ||
|image = | |image = | ||
|imagecaption= | |imagecaption= | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|date = 2020 census | |date = 2020 census | ||
|ref = | |ref = | ||
|familycolor = | |familycolor = n | ||
|family = [[List of language families#Language isolates|Language isolate]] or one of | |family = [[List of language families#Language isolates|Language isolate]] or one of Sahar's primary [[List of language families#Language families|language families]] | ||
|ancestor = [[Proto-Vemkha]] | |ancestor = [[Proto-Vemkha]] | ||
|dia1 = Vemgha | |dia1 = Vemgha | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|glotto = | |glotto = | ||
|glottorefname= | |glottorefname= | ||
|map = Vemkha map.png | |||
|mapsize = 220px | |||
|mapcaption = Approximate distribution of Vemkha speakers | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Vemkha''' (Vemkha: ''Vəmɣa'' [[Vemkha languages#Phonology|[vəmɣa]]], '' | '''Vemkha''' (<small>Vemkha</small>: ''Vəmɣa'' [[Vemkha languages#Phonology|[vəmɣa ɣuɣs]]], ''Wamx'' [[Vemkha languages#Phonology|[wamx kuɣs]]] or ''Vəŋx'' [[Vemkha languages#Phonology|[vəŋx kuɣs]]]) is a [[List of language families#Language_isolates|language isolate]] or small [[List of language families#Language_families|language family]] spoken by the [[Vemkha people]] of [[Kasiiralq]]. | ||
==Languages== | |||
[[Category:Languages]][[Category:Language isolates]][[Category:Language isolates of Northern Miraria]][[Category:Language families]][[Category:Language families of Northern Miraria | ==Classification== | ||
The classification of Vemkha has been highly controversial. It has not been conclusively proven to be related to any other language family, despite numerous attempts by linguists. Most attempts have focused on geographically proximate families, such as [[Tulipi-Lakup languages|Tulipi-Lakup]], [[Maakpauean languages|Maakpauean]], [[Yucho languages|Yucho]], [[East Mirarian languages|East Mirarian]] or [[Shaelic languages|Shaelic]]. Other proposals have focused on more distant connections, such as the [[Amaian languages]] of eastern Vaniu, the [[Maithic languages]] of Central Miraria and even the [[Darkinic languages]] of northern [[Soltenna]]. | |||
==History== | |||
==Phonology== | |||
===Consonants=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" | |||
|+Vemkha consonants | |||
! colspan="2" | | |||
! Labial | |||
! Dental | |||
! Alveolar | |||
! Palatal | |||
! Velar | |||
! Uvular | |||
! Glottal | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="2" | Nasal | |||
| m | |||
| n̪ | |||
| n | |||
| ɲ | |||
| ŋ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="3" | Stop | |||
! <small>plain</small> | |||
| p | |||
| t̪ | |||
| t | |||
| c | |||
| k | |||
| q | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! <small>aspirated</small> | |||
| pʰ | |||
| t̪ʰ | |||
| tʰ | |||
| cʰ | |||
| kʰ | |||
| qʰ | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! <small>voiced</small> | |||
| (b) | |||
| (d̪) | |||
| (d) | |||
| (ɟ) | |||
| (ɡ) | |||
| (ɢ) | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="2" | Fricative | |||
! <small>voiceless</small> | |||
| f | |||
| θ | |||
| colspan="2" | s ~ ʃ ~ ɕ | |||
| x | |||
| χ | |||
| h | |||
|- | |||
! <small>voiced</small> | |||
| v | |||
| ð | |||
| colspan="2" | z ~ ʒ ~ ʑ | |||
| ɣ | |||
| ʁ | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="2" | Approximant | |||
| | |||
| l̪ | |||
| l | |||
| j | |||
| w | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="2" | Trill | |||
! <small>voiceless</small> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| r̥ | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! <small>voiced</small> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| r | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
Vemkha is notable for its six-way distinction in obstruents, distinguishing labial, dental, alveolar, palatal, velar and uvular plosives and fricatives. All plosives show a two way distinction between voiceless aspirated and unaspirated, although many varieties have innovated voiced plosives from former clusters between nasals and unaspirated stops. This may also apply across word boundaries. | |||
The full 6-way phonemic distinction is limited in many positions. The distinction between uvular and velar consonants is neutralised in onset position in roots: uvulars appear before the vowels /a o/ while velars appear before the vowels /i e ə u/. However, the distinction remains phonemic in codas (including when a coda is converted into an onset by a following suffix). | |||
The distinction between dental and alveolar fricatives is also limited: neither can appear in a cluster with the other, and regressive assimilation will occur in order to prevent this. This restriction applies to both obstruents and sonorants. | |||
==Further Reading== | |||
{{Language families of Miraria}} | |||
{{Language families}} | |||
[[Category:Vemkha language]][[Category:Languages]][[Category:Language isolates]][[Category:Language isolates of Northern Miraria]][[Category:Language families]][[Category:Language families of Northern Miraria]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 16 October 2022
| Vemkha | |
|---|---|
| Vəmɣə ɣuɣs, Vəŋx kuɣs, Wamx kuɣs | |
| Pronunciation | [vəmɣə], [wamx], [vəŋx] |
| Region | Kasiiralq |
| Ethnicity | 6,430 Vemkha |
| Native speakers | c. 6,400 (2020 census) |
| Language family | Language isolate or one of Sahar's primary language families |
| Early forms: | Proto-Vemkha
|
| Dialects | Vemgha
Vamkh
Vengkh
|
| CWS code | VMKH |
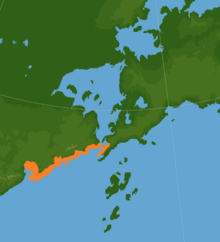 Approximate distribution of Vemkha speakers | |
Vemkha (Vemkha: Vəmɣa [vəmɣa ɣuɣs], Wamx [wamx kuɣs] or Vəŋx [vəŋx kuɣs]) is a language isolate or small language family spoken by the Vemkha people of Kasiiralq.
Languages
Classification
The classification of Vemkha has been highly controversial. It has not been conclusively proven to be related to any other language family, despite numerous attempts by linguists. Most attempts have focused on geographically proximate families, such as Tulipi-Lakup, Maakpauean, Yucho, East Mirarian or Shaelic. Other proposals have focused on more distant connections, such as the Amaian languages of eastern Vaniu, the Maithic languages of Central Miraria and even the Darkinic languages of northern Soltenna.
History
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n̪ | n | ɲ | ŋ | |||
| Stop | plain | p | t̪ | t | c | k | q | |
| aspirated | pʰ | t̪ʰ | tʰ | cʰ | kʰ | qʰ | ||
| voiced | (b) | (d̪) | (d) | (ɟ) | (ɡ) | (ɢ) | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | θ | s ~ ʃ ~ ɕ | x | χ | h | |
| voiced | v | ð | z ~ ʒ ~ ʑ | ɣ | ʁ | |||
| Approximant | l̪ | l | j | w | ||||
| Trill | voiceless | r̥ | ||||||
| voiced | r | |||||||
Vemkha is notable for its six-way distinction in obstruents, distinguishing labial, dental, alveolar, palatal, velar and uvular plosives and fricatives. All plosives show a two way distinction between voiceless aspirated and unaspirated, although many varieties have innovated voiced plosives from former clusters between nasals and unaspirated stops. This may also apply across word boundaries.
The full 6-way phonemic distinction is limited in many positions. The distinction between uvular and velar consonants is neutralised in onset position in roots: uvulars appear before the vowels /a o/ while velars appear before the vowels /i e ə u/. However, the distinction remains phonemic in codas (including when a coda is converted into an onset by a following suffix). The distinction between dental and alveolar fricatives is also limited: neither can appear in a cluster with the other, and regressive assimilation will occur in order to prevent this. This restriction applies to both obstruents and sonorants.